When it comes to swimwear, style and comfort are important, but so is protection from the sun’s harmful UV rays. UV protection swimsuits have become a popular choice, especially as awareness of skin health grows. But how is the UV protection of these swimsuits measured, and what standards do manufacturers follow? Let’s dive into the key UV protection standards for swimsuits worldwide and why they matter.
Why UV Protection Matters in Swimwear?
account for about 6% of sunlight, wavelength range: of 200~400nm, and are mainly divided into three categories.
Among them:
1. Ultraviolet A (UVA): Wavelength 320~400nm, 95%-98% of the total ultraviolet rays, with low energy, which can penetrate glass, certain clothes, and human epidermis, and can penetrate under the dermis and react with the dermis, gradually destroying the elasticity of the skin, making the skin loose, wrinkles appear, and accelerating its ageing.
2. Ultraviolet B (UVB): Wavelength 290~320nm, 2%~5% of the total ultraviolet rays, with high energy, which can penetrate the human epidermis. It is the culprit for sunburn, skin tumours and immunosuppression.
3. Ultraviolet C (UVC): Wavelength 200~290nm, the highest energy and the strongest damaging type of UV radiation. However, it is almost completely absorbed by the ozone layer and will not cause harm to humans.
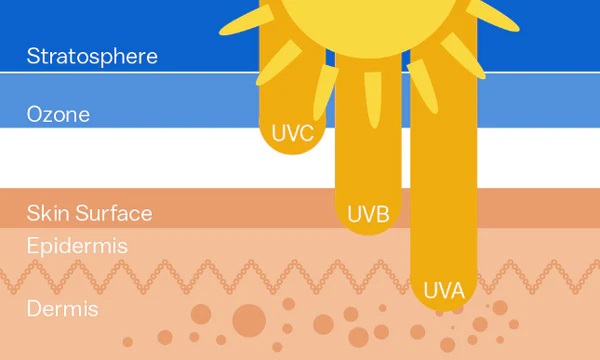
In recent years, due to the large-scale emission of chlorofluorinated compounds such as Freon in human production and life, the atmosphere has been increasingly damaged, the amount of ultraviolet radiation reaching the ground has increased, and the number of diseases caused by excessive ultraviolet radiation has increased.
Under normal circumstances, the safe amount of ultraviolet radiation that human skin can receive should be within 20kJ/㎡ per day, while the amount of ultraviolet radiation reaching the ground is 40~60kJ/㎡ on cloudy days, 80~100kJ/㎡ on sunny days, and can reach 100~200kJ/㎡ on hot summer days. The shielding rate of ordinary clothing against ultraviolet rays is generally around 50%, which is far from meeting the protection requirements. In addition, long-term ultraviolet radiation can also cause textiles to fade and age. Therefore, it is necessary to add UV protection to swimwear and other textiles.
UV Protection Standards for Swimwear
UV protection in swimwear is measured using the UPF (Ultraviolet Protection Factor) rating, which indicates how much UV radiation is blocked by the fabric. For example, a UPF 50 fabric allows only 1/50th (or 2%) of UV rays to pass through, effectively blocking 98% of harmful radiation.
But how is this performance tested? Although there isn’t a globally unified testing standard for UV protection textiles, several recognized standards guide swimwear manufacturers in testing and labelling UV-protective swimwear:

1. Australia/New Zealand Standard: AS/NZS4399:1996 (Sun protective clothing-Evaluation and classification)
One of the most stringent standards, it requires swimwear to have a UPF rating of 50+ to be labelled as “excellent UV protection.” This means the fabric blocks at least 98% of harmful UV radiation.
2. EU Standard: EN13758-1:2001 (Textiles-Solar UV protective properties-Part 1:Method of test for apparel fabrics)
This standard evaluates UV protection by calculating the UPF (Ultraviolet Protection Factor) of textiles. A UPF of 40 or higher is typically considered excellent, blocking over 97.5% of UV rays.
3. US Standard: AATCC183-2010 (Transmittance or Blocking of Erythemally Weighted Ultraviolet Radiation through Fabrics)
This American standard uses advanced spectrophotometers to measure the UV transmittance of fabrics and provides a UPF rating based on the fabric’s effectiveness in blocking UV rays.
4. China National Standard: GB/T18830-2009 (Evaluation For Solar Ultraviolet Radiation Protective Properties)
The Chinese standard ensures that textiles labelled as UV-protective meet specific thresholds, with rigorous testing to measure their UPF values.
Parameter comparison table for each UV protective test standard
| Standard | AS/NZS4399 | EN13758 | AATCC183 | GB/T18830 |
| Application | Sun-protective fabrics, clothing, and gear that are designed to be worn close to the skin | Garment Fabrics | All textiles | All textiles |
| Wavelength Range | 290nm – 400nm | 290nm – 400nm | 280nm – 400nm | 290nm – 400nm |
| Number of samples | 2 warp, 2 weft | 4 | 2 wet, 2 dry | 4 dry |
| Non-homogeneous samples | Each color and each expected result should have at least 1 sample | Each color and expected result should have at least 2 samples | Each color and each expected result should have at least 1 sample. | Each color and expected result should have at least 2 samples |
| Humidity Control | (20 ± 5)°C, (50 ± 2)% RH | (20 ± 2)°C, (65 ± 2)% RH | (21 ± 1)°C, (65 ± 2)% RH | (20 ± 2)°C, (65 ± 2)% RH |
| Test Results | Sample UPF value, the average UPF value, the average transmission rates for UVA and UVB, UPF rating | Sample UPF value, the average UPF value, the average transmission rates for UVA and UVB, UPF rating | Sample UPF value, average transmission rates for UVA and UVB, And blocking rates for UVA and UVB. | Sample UPF value, the average UPF value, the average transmission rates for UVA and UVB |
How UV Protection Is Tested?
The testing methods across these standards share common features:

1. Stable UV Light Source: A UV light source emits rays with wavelengths between 290nm and 400nm.
2. Spectral Analysis: The fabric sample is exposed to these rays through a monochromator, which isolates specific wavelengths.
3. Measurement: The amount of UV light that passes through the fabric is measured, and the UPF value is calculated based on the percentage of UV rays blocked.
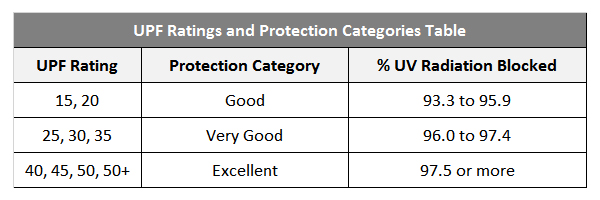 A higher UPF rating means better protection, with ratings typically categorized as:
A higher UPF rating means better protection, with ratings typically categorized as:
UPF 15-24: Good protection
UPF 25-39: Very good protection
UPF 40-50+: Excellent protection
UV Protection Swimwear at Unijoy Custom Swimwear Manufacturer
At Unijoy, we’re committed to providing high-quality UV protection swimwear that meets the standards of various countries. Our fabrics are rigorously tested to ensure they block harmful UV rays while remaining comfortable, durable, and stylish. We offer customizable swimwear manufacturing solutions, allowing you to choose the design, fabric, and features that suit your brand and your customer’s needs. Whether you’re targeting markets in the EU, Australia, the US, we ensure your UV-protective swimwear meets the required standards.
Understanding UV protection standards is essential for anyone producing or purchasing swimwear. With the right knowledge, you can ensure your swimwear not only looks great but also provides essential protection against harmful UV rays.
UV Protection Custom Swimwear
Sun-protective Custom Bikini UPF50+ One-piece Swimsuit UV Rash Guard Swim Shirt Uv Protection Swim Shorts
Want to learn more about UV-protective swimwear or create your own line?
Contact Unijoy today for professional manufacturing and customization services tailored to your needs.









